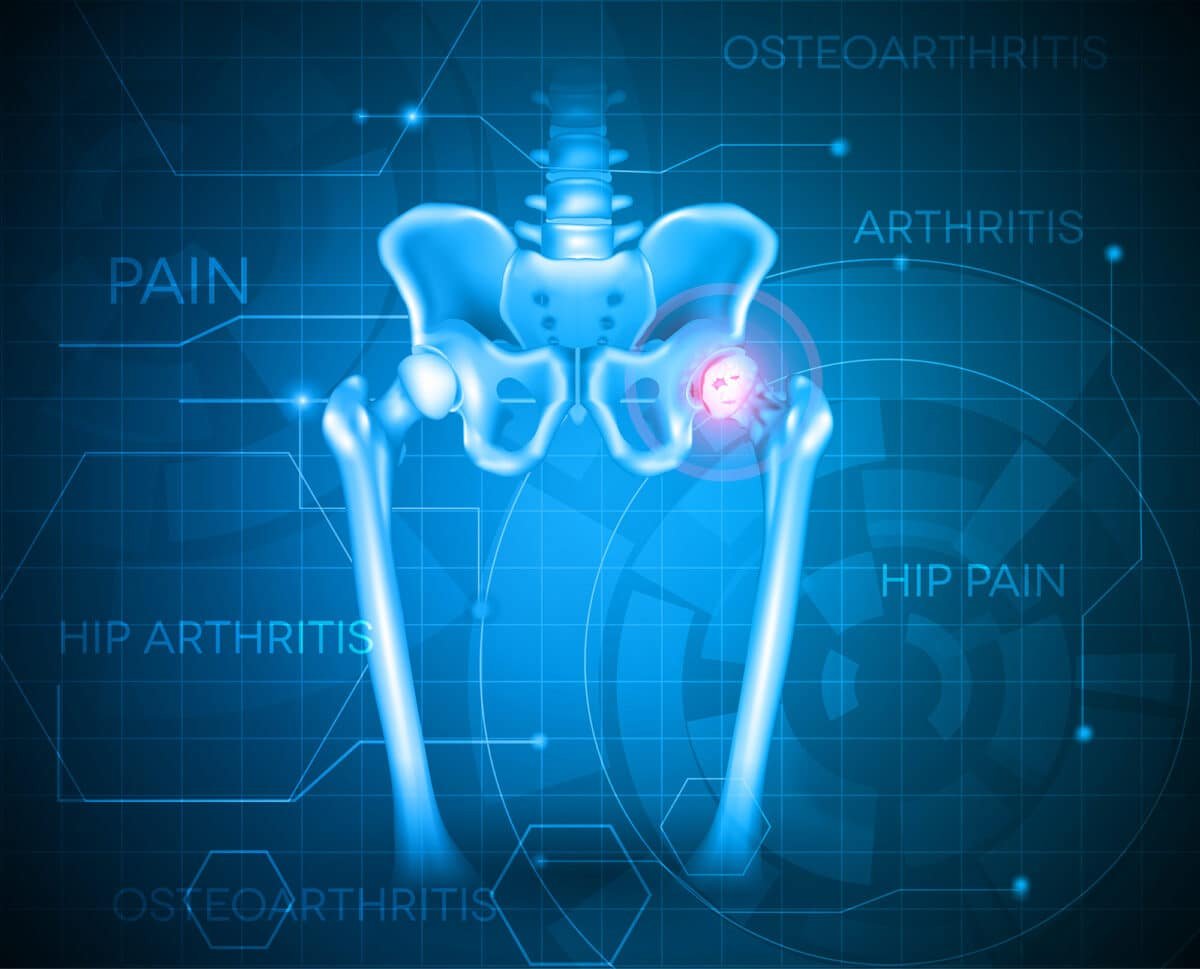
Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and turning require the use of your hip and knee joints.
ΑΡΘΡΑ
Partial knee arthroplasty (PTA) is a surgical procedure that helps relieve arthritis in one or two of the three compartments of the knee.
Total knee replacement is a surgical procedure during which a pathological or damaged joint is replaced by an artificial joint called an implant.
What is robotic hip replacement?
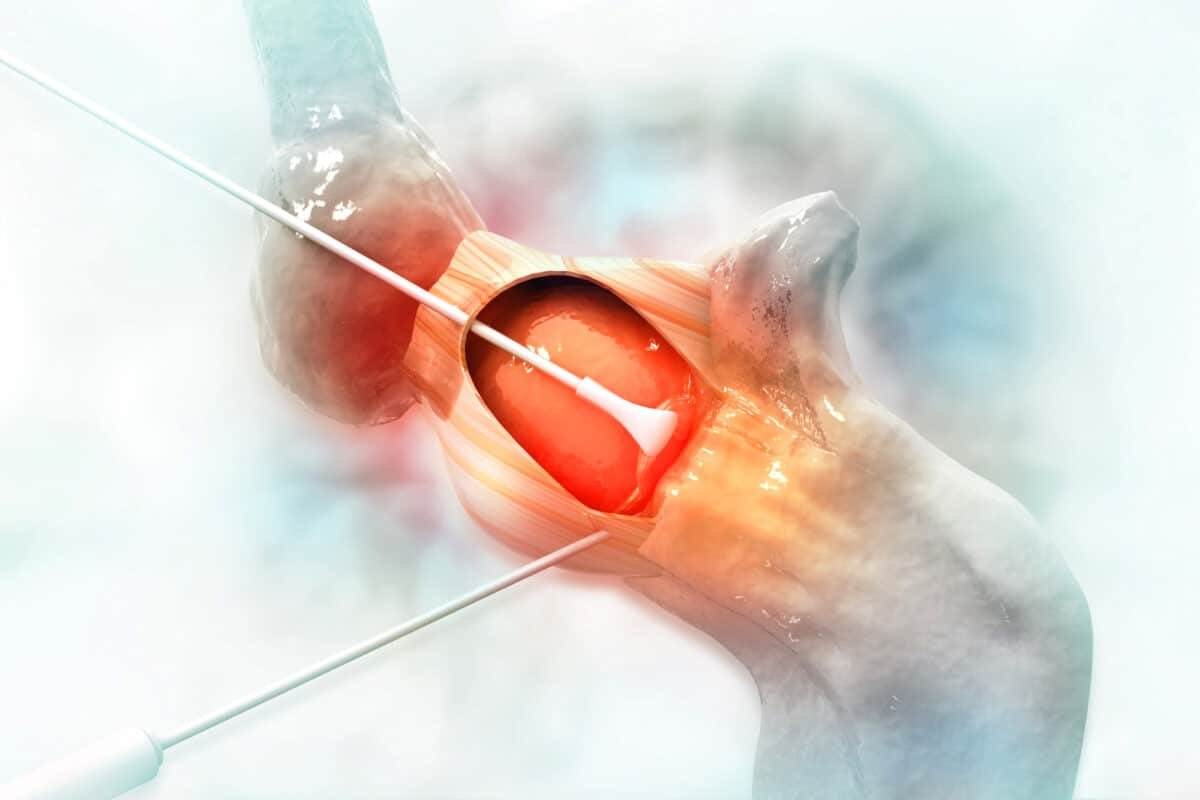
A robotic hip replacement is similar to a traditional hip replacement. The surgeon removes the damaged tissue in your hip and replaces it with an artificial joint. The difference is that it is done with the help of a robotic arm. Robotic-assisted procedures allow for greater precision and can lead to shorter recovery times and better results.
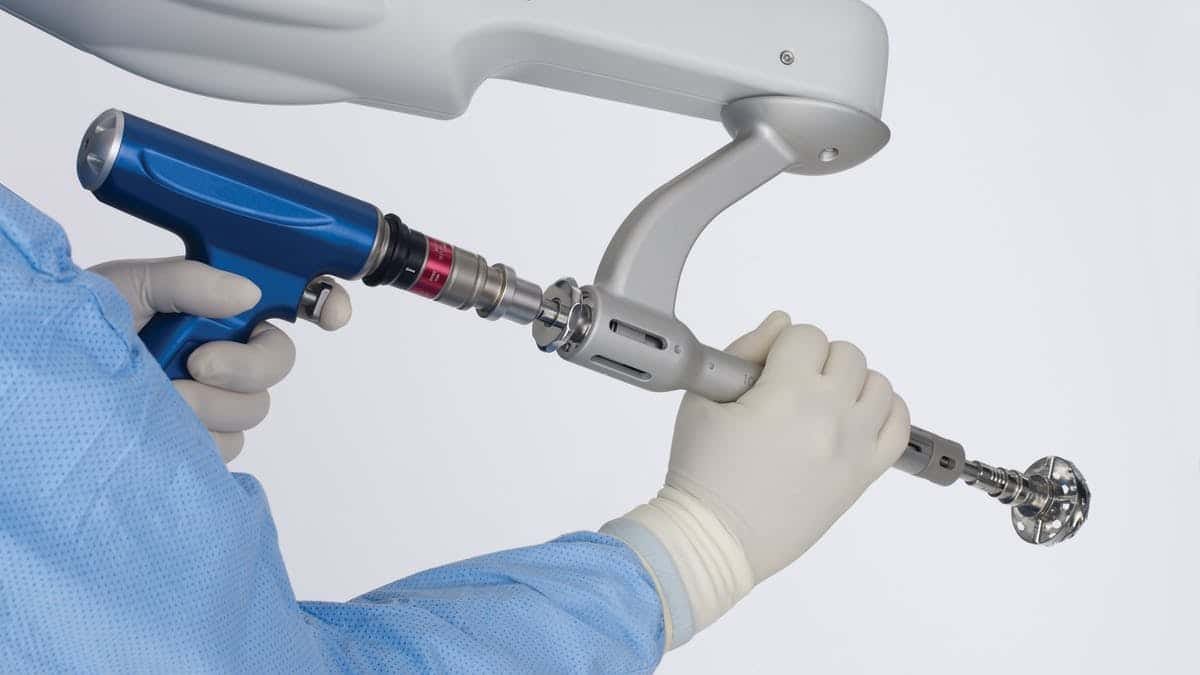
How do Mako hip replacements work?
If your orthopedic surgeon recommends a Mako hip replacement procedure, the first step is to take pictures of your joint that will be used to plan your surgery.
These images are so accurate that your surgeon can determine the best approach before you enter the operating room. The scans take into account your bone structure, hip joint alignment and surrounding tissues. This helps your surgeon plan every step of your surgery, including choosing the best implant size, location and placement.
When the time comes for your Mako hip replacement, your surgeon will place the Mako arm according to the measurements and use the robotic tool throughout the procedure. Mako does not perform surgery on its own. Instead, it acts as a guide, helping your surgeon follow the plan he has in advance. This means more precise incisions, optimal placement and in many cases better and faster recovery.
After surgery, your surgeon and the rest of the care team will monitor your progress and plan a course for your recovery at home. Your surgeon will discuss all the options available to you, including whether you are a good candidate for robotic joint replacement.
Benefits of robotic hip replacement
The benefits of robotic hip replacement surgery compared to traditional surgery include:
- Improved surgical planning
- Greater accuracy
- Optimal joint alignment
Hip pain that may qualify for robotic surgery
If you have hip pain that interferes with your daily activities and non-surgical options have not helped, you may be eligible for robotic hip replacement surgery. If you are a candidate for traditional hip replacement, you may also be a candidate for robotic-assisted hip replacement. Your doctor will work with you to determine the best option for your individual needs.
Rehabilitation process after robotic hip replacement
Mako uses more precise incisions and helps achieve optimal joint alignment, which can lead to better and faster recovery. After surgery, your surgeon will monitor your progress and plan a course for your recovery at home.
The video belongs to the channel Your Medical Doctor
The syndrome is called when the muscles or tendons of the lower abdominal wall weaken. The location of the pain is in the inguinal region of the abdominal wall, where the "classic" inguinal hernia also occurs.
Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and turning require the use of your hip and knee joints.
A patellar tendon tear is a significant injury affecting the tendon that connects the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia). The patellar tendon works in conjunction with the muscles in the front of the thigh to extend the knee, enabling actions such as kicking, running, and jumping. A tear in this tendon can severely impair knee function and mobility.
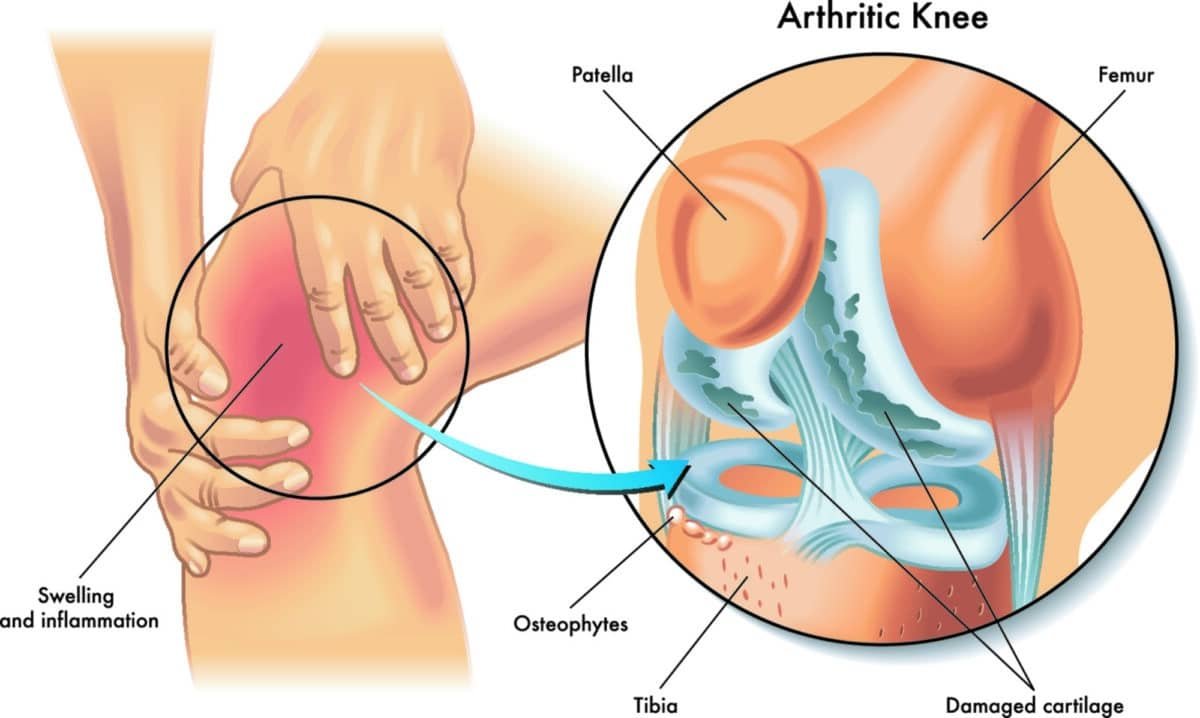
A meniscus tear is a common knee injury involving the tearing of one of the two C-shaped pieces of cartilage that act as shock absorbers between the thighbone (femur) and the shinbone (tibia). These pieces of cartilage, known as the medial and lateral menisci, help to distribute weight across the knee joint and provide stability.
To diagnose a rotator cuff tear you may need careful examination by an orthopedic surgeon. You may also need further diagnostic tests such as x-ray and MRI.
It is very common in children from 1 to 12 years old. It is the Transient, auto-infectious inflammation of the synovial membrane.