Arthroscopy – Sports Injuries – Arthroscopic Surgery
What is Arthroscopy?

Arthroscopy is a specialized technique used to diagnose and treat joint problems. This procedure allows the orthopedic surgeon to examine the inside of a joint with great precision and to carry out possible operations, without the need for a large incision as in the classic methods used in the past.
The arthroscopy procedure involves inserting a thin tube through a small incision in the skin. This tube is connected to a fiber-optic video camera, which transmits images of the inside of the joint to a high-definition screen. This allows the surgeon to see any changes, lesions or problems that may be affecting the function of the joint and to prepare for the surgical procedure.
An orthopedic surgeon can even repair certain types of joint damage during arthroscopy, using special surgical tools inserted through additional small incisions. This operation can allow damage such as broken pieces of cartilage, bone fragments or small cracks to be repaired or removed.
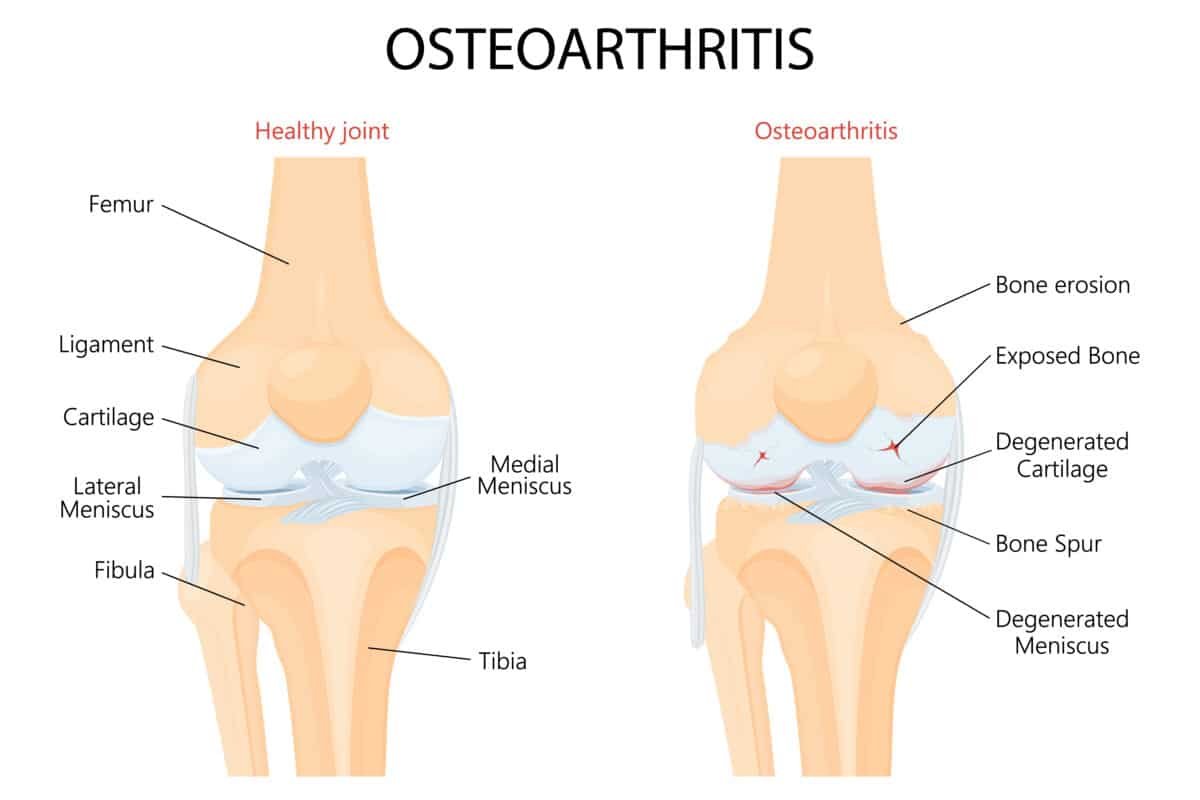
Diseases and injuries can damage the bones, cartilage, ligaments, muscles and tendons in the joints.
To diagnose your condition, the doctor will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination. In addition, he will usually order x-rays to get a picture of your joints. For some cases, such as suspected bone destruction or a need for more detailed imaging, an additional imaging modality such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) may need to be performed. Your bones, cartilage, ligaments, muscles and tendons can be damaged by disease and injury. After diagnosis, your doctor will determine the most appropriate treatment option for your condition.
Total cost of arthroscopy
One of the important factors influencing the decision to have arthroscopy is the overall cost of the procedure. The total cost of arthroscopy includes various elements and may vary depending on the materials used, the hospital – clinic where the operation is performed.
It is important to note that the total cost of arthroscopy can vary significantly from case to case. Factors such as insurance, additional tests and post-operative treatments can affect the total cost. It is important to discuss the matter with your doctor and get quotes from various sources in order to understand and prepare for the total cost of arthroscopy.
Conditions most commonly discovered with arthroscopy?
The following are the conditions most often discovered during an arthroscopic procedure:
- Inflammation. This includes the lining (joint membrane) of the knee, shoulder, elbow, wrist or ankle
- Injuries. These include the following:
- Rotator cuff tears, impingement syndrome and recurrent shoulder dislocations
- Meniscus (cartilage) tears, chondromalacia (cartilage pad wear or injury), and ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) with knee instability
- Pieces of loose bone or cartilage. This is especially in the knee, shoulder, elbow, ankle or wrist.
When is it happening?
Doctors use arthroscopy to help diagnose and treat a variety of joint conditions, most commonly those affecting:
- the knee
- the shoulder
- the elbow
- the ankle
- the hip
What are the advantages of arthroscopy?

Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that presents several advantages compared to open surgery. The following are mentioned:
- Faster recovery: Because the incisions required for arthroscopy are small, patients typically recover faster than with traditional open surgery. This means recovery time can be significantly shorter, allowing patients to return to their daily activities more quickly.
- Less pain: Due to the small size of the incisions, arthroscopy usually causes less pain compared to traditional procedures. This helps improve patient comfort after the procedure and reduces the need for strong pain medications.
- Minimal blood loss and scarring: Due to the small size of the incisions, arthroscopy usually involves minimal blood loss during the procedure. Also, the scars caused are very small and are often removed a few weeks after surgery.
- Minimal risk of infectious complications: Due to the small incision and minimal tissue intervention, the risk of infectious complications is usually much lower compared to open surgery.
Overall, arthroscopy provides an advanced method of diagnosing and treating joint problems, with minimal surgery and a quick recovery for the patient. However, the appropriate method of treatment will depend on the nature and severity of the joint problem, as well as your doctor’s systematic evaluation.
Risks
Although arthroscopy is a relatively safe procedure, there are some risks and potential complications that can occur. Although these complications are uncommon, it is important to be aware of the potential risks. Some of the problems that may include are:
- Tissue or nerve damage: During arthroscopy, the placement of instruments and their movement within the joint can, in rare cases, cause damage to surrounding tissues or nerves. However, the doctors who perform the procedure are skilled and try to reduce this risk to a minimum.
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection. Open surgeries increase the risk of infection compared to arthroscopy, but even arthroscopy is not completely free of this risk. Doctors take steps to reduce the risk of infection, such as using antiseptics and following strict hygiene rules.
- Allergic reaction to anesthesia.
- Excessive bleeding or swelling.
- Blood clots: Rarely, but when the arthroscopy procedure lasts longer than an hour, there is an increased risk of developing blood clots in the legs or lungs. To reduce this risk, doctors may advise patients to take preventive measures, such as wearing elastic stockings or taking antiplatelet medications.
How to prepare?
The type of anesthesia used varies depending on the procedure.
- Local anesthesia. Anesthesia is injected under the skin to block feeling in a limited area, such as your knee. You will be awake during the arthroscopy, but the most you will feel is pressure or a sense of movement within the joint.
- Regional anesthesia. The most common form of regional anesthesia is given through a small needle placed between two of the vertebrae in your spine. This numbs the lower half of your body, but you stay awake.
- General anesthesia. Depending on the length of the operation, it may be best for you to be unconscious during the procedure. General anesthesia is given through a vein (intravenously).
What can you expect?
Although the arthroscopy experience can vary depending on the reason the procedure is being performed and the joint involved, there are some common features you can expect. When you arrive at the hospital or clinic, you will be asked to remove your clothing and jewelry and change into a hospital gown. This is done to ensure an absolutely clean and safe environment to carry out the process.
A nurse will then place an IV catheter in your arm so that medicines or fluids can be given during the procedure. You may also be given an injection of a sedative or anesthetic medicine to help with your comfort and tolerance during the procedure and to prevent any problems. This is to ensure that you feel as little pain and discomfort as possible during the arthroscopy.
It is important to note that this is a general description and the details may vary depending on the doctor, hospital or clinic where the arthroscopy is performed. It is important to discuss with your doctor the details of the procedure and any concerns you may have so that you have a better understanding of the specific procedure.
What is the role of the surgeon and how is his experience affected by the arthroscopic technique?
The role of the surgeon in arthroscopic surgery is vital and requires specialized knowledge and skills. The surgeon’s experience is greatly influenced by the arthroscopic technique as he develops a deep understanding of the advantages and limitations associated with it.
An orthopedic surgeon must be familiar with the use of the arthroscope, the special tools, and the technique required to perform an arthroscopic procedure. The surgeon watches the image transmitted by the arthroscope’s camera, allowing him to examine the joint space and possible diseases with great precision.
The surgeon must have specialized training and experience to perform arthroscopic procedures accurately and safely. Becoming familiar with the arthroscopic technique requires many hours of training and practice. The surgeon must learn to control the fine movements of his hands and work harmoniously with his team, including the physician operating the arthroscope.
The arthroscopic technique allows the surgeon to achieve high precision and minimal intervention in the surrounding tissues. This means that the surgeon must have an accurate understanding of the anatomy of all joints and adjacent structures, as well as the ability to perform the operation safely and accurately.
In addition, the surgeon must be able to deal with possible complications and difficulties that may arise during arthroscopic surgery. This requires composure, dexterity and the ability to adapt to new situations during the operation.
The experience of the surgeon is critical to the success of arthroscopic surgery. As the surgeon gains more experience in the arthroscopic technique, the speed and precision of his movements increases. Also, his experience helps him more easily recognize conditions and cases that can benefit from arthroscopic surgery.
However, it is important to note that experience is not acquired by itself. The surgeon must maintain abreast of the latest developments in arthroscopic technology and techniques, participate in educational programs, and maintain close collaboration with other specialists in the field.
What are the types of arthroscopy?
Surgeons use arthroscopy to see inside joints without having to make large incisions. Types of arthroscopy include:
- Elbow arthroscopy.
- Foot and ankle arthroscopy.
- Arthroscopy of the hand and wrist.
- Hip arthroscopy.
- Knee arthroscopy.
- Shoulder arthroscopy.
The type of anesthesia used varies depending on the procedure.
- Local anesthesia. Anesthesia is injected under the skin to block feeling in a limited area, such as your knee. You will be awake during the arthroscopy, but the most you will feel is pressure or a sense of movement within the joint.
- Regional anesthesia. The most common form of regional anesthesia is given through a small needle placed between two of the vertebrae in your spine. This numbs the lower half of your body, but you stay awake.
- General anesthesia. Depending on the length of the operation, it may be best for you to be unconscious during the procedure. General anesthesia is given through a vein (intravenously).
One technique to improve the look inside your joint involves filling the joint with a sterile fluid. This expands the area around the joint. A small incision is made for the projection device. Additional small incisions at different points around the joint allow the surgeon to insert surgical tools to repair the joint. The incisions will be small enough to be closed with one or two stitches or narrow strips of sterile tape.
After the procedure
Arthroscopic surgery usually takes a relatively short time. For example, knee arthroscopy takes about an hour. After the procedure is complete, you will be taken to a separate room to recover for a few hours before returning home and continuing your daily routine.
Then, your care after arthroscopy may include:
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It is important to take the medicines as directed by the doctor.
- Rest: At home, you will need to rest and avoid excessive activity. You may be advised to rest in bed, elevate and compress the joint, and apply ice or cold compresses to reduce swelling and pain.
- Protection: You may need to use temporary splints, crutches, or other devices to comfort and protect the joint during recovery.
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation: Your doctor may recommend that you begin physical therapy and rehabilitation to strengthen your muscles, improve joint function, and return to your daily activities. It is important to follow the physiotherapist’s instructions and not to overdo the activity you undertake.
In addition, if you develop any of the following symptoms, you should contact your surgeon:
- Fever.
- Pain that is not relieved by your prescribed medications.
- Redness or swelling in the area of the arthroscopy.
- New numbness or tingling in the arthroscopy area.
These symptoms may indicate possible complications or other problems that should be evaluated by your doctor. Work closely with your orthopedic surgeon and follow his or her instructions for recovery and resumption of daily activities.
When will I know the results of an arthroscopic procedure?
After arthroscopic surgery, it’s normal to wonder when you’ll know the results. Your doctor will explain the healing progress and joint recovery.
The time frame for obtaining results from an arthroscopic procedure may vary depending on the type of procedure, the area of the body affected, and each patient’s individual normal recovery time. It is important to note that everyone responds differently to surgery and recovery time can vary.
Immediately after arthroscopic surgery, you may feel relief from the pain or discomfort caused by the original joint problem. However, the full effects of the surgery may take longer to appear.
Doctors usually provide instructions and information about the recovery and progress of the operation. Some factors that can affect recovery time include age, general health, severity of the joint problem, and following the doctor’s instructions.
How is recovery after arthroscopy?
Small puncture wounds take several days to heal. The surgical dressing can usually be removed the morning after surgery and adhesive tapes can be applied to cover the small healing incisions.
Although puncture wounds are small and pain in the arthroscopy joint is minimal, it takes several weeks for the joint to fully recover. A specific activity and rehabilitation program may be recommended to speed your recovery and protect future joint function.
It is not unusual for patients to return to work or school or resume daily activities within a few days. Athletes and others who are in good physical condition can, in some cases, return to sports activities within a few weeks. Remember, however, that people undergoing arthroscopy can have many different diagnoses and pre-existing conditions, so each patient’s arthroscopic procedure is unique to that person. Recovery time will reflect this individuality.
Usually, the doctor will schedule a review after surgery to assess progress and give you more information about the healing and recovery of the joint. This review may include x-rays or other tests to assess the condition of the joint.
It is important to be patient during recovery and follow your doctor’s instructions regarding incision care and recovery. In case you experience any concern or unexpected development, you should contact your doctor immediately.
Each case of arthroscopic surgery is unique and recovery times may vary. Your doctor will be the best guide in assessing the results and informing you about the recovery time of the particular arthroscopic procedure.
Driving after arthroscopy
Driving after arthroscopy is a concern for many patients who have undergone this procedure. Arthroscopy may be required to correct problems in joints such as the knee or ankle, and recovery is important to restore normal joint function.
Doctors usually recommend not driving immediately after arthroscopy and wait until your joint has recovered and you have full control. It will usually take a few weeks or even months, depending on the severity of the operation and individual recovery time.
When you decide to resume driving, it is important that you have fully recovered and have full mobility and control of the joint. Also, you must have consulted your doctor and received their approval to resume driving. Remember that driving requires physical and mental concentration, and it is important that you are able to meet the demands of driving safely.
Finally, it is important to pay attention to any restrictions or suggestions you have received from your doctor about driving after arthroscopy. Follow your doctor’s instructions and let him know about any concerns or problems you may have while driving.
Sports and activities you can do after knee replacement?
We recommend specific activities for TKA patients, which include:
- Cycling: Riding a bicycle outdoors or using a stationary bike indoors is a great way to strengthen your new knee. It is best to start at level or using a lower volume.
- Swimming: Enjoying the pool won’t strain your joints and you can get an aerobic workout. You can start swimming once your stitches are removed and the wound has healed.
- Walking and hiking: Walking is highly recommended for your recovery. If you are a runner, you may want to enjoy the lower impact of walking after a knee replacement.
- Calisthenics: It’s good to keep your body in shape with low-impact strength and flexibility training. While you may enjoy Zumba, you should stick with lower impact movements and avoid twisting movements.
- Low Resistance Weight Lifting: Keeping your muscles toned is an important component of fitness.
- Low-resistance rowing: You’ll get a good upper-body workout, but you’ll need to set up the machine so your knees are more than 90 degrees.
- Skis and elliptical machines: Like cycling, there is no impact, but you can get a good aerobic workout.
Strengthening exercises after arthroscopy
After an arthroscopy, strengthening exercises are an important part of joint rehabilitation and recovery. These exercises aim to strengthen the muscles around the joint, helping to restore strength, flexibility and functionality to the joint.
The execution of these exercises must be done under the supervision of a specialist therapist or physiotherapist, who will adapt the exercise program according to the needs and capabilities of each patient.
Strength training can include the use of rubber bands or free weights, as well as bodyweight exercises. These exercises promote the development of strength and flexibility in muscles and joints. You usually start with simple exercises and gradually increase the intensity and number of repetitions as you progress in your recovery.
It is important to follow the instructions of the specialist and not to exaggerate the intensity and duration of the exercises, as this can cause complications or slow down the recovery.
Strengthening exercises after an arthroscopy are an essential means of regaining function and improving quality of life. By performing these exercises consistently and correctly, you can strengthen the joint and return to daily activities and sports with safety and confidence.
Results
In general, arthroscopy usually allows patients to return to their daily activities in a relatively short time. After the procedure, you should be able to return to the office and resume work in a few days. You may also be allowed to drive again after one to three weeks, and you can return to more vigorous activity after a few weeks.
However, it is important to mention that recovery after arthroscopy varies depending on the patient’s condition and the extent of the operation. Some patients may need a longer period of recovery and rehabilitation depending on the type and degree of disease affecting their joint.
The orthopedic surgeon who performed the arthroscopy will review the findings and results of the procedure with you as soon as possible. He can provide you with a written report about your findings and progress. You will also have follow-up visits with your doctor to monitor your progress and get any further treatment care or advice you may need.
- Category
- Services

